Download files at the bottom of the page |
See video on how to add Shim Paper routine into your project |
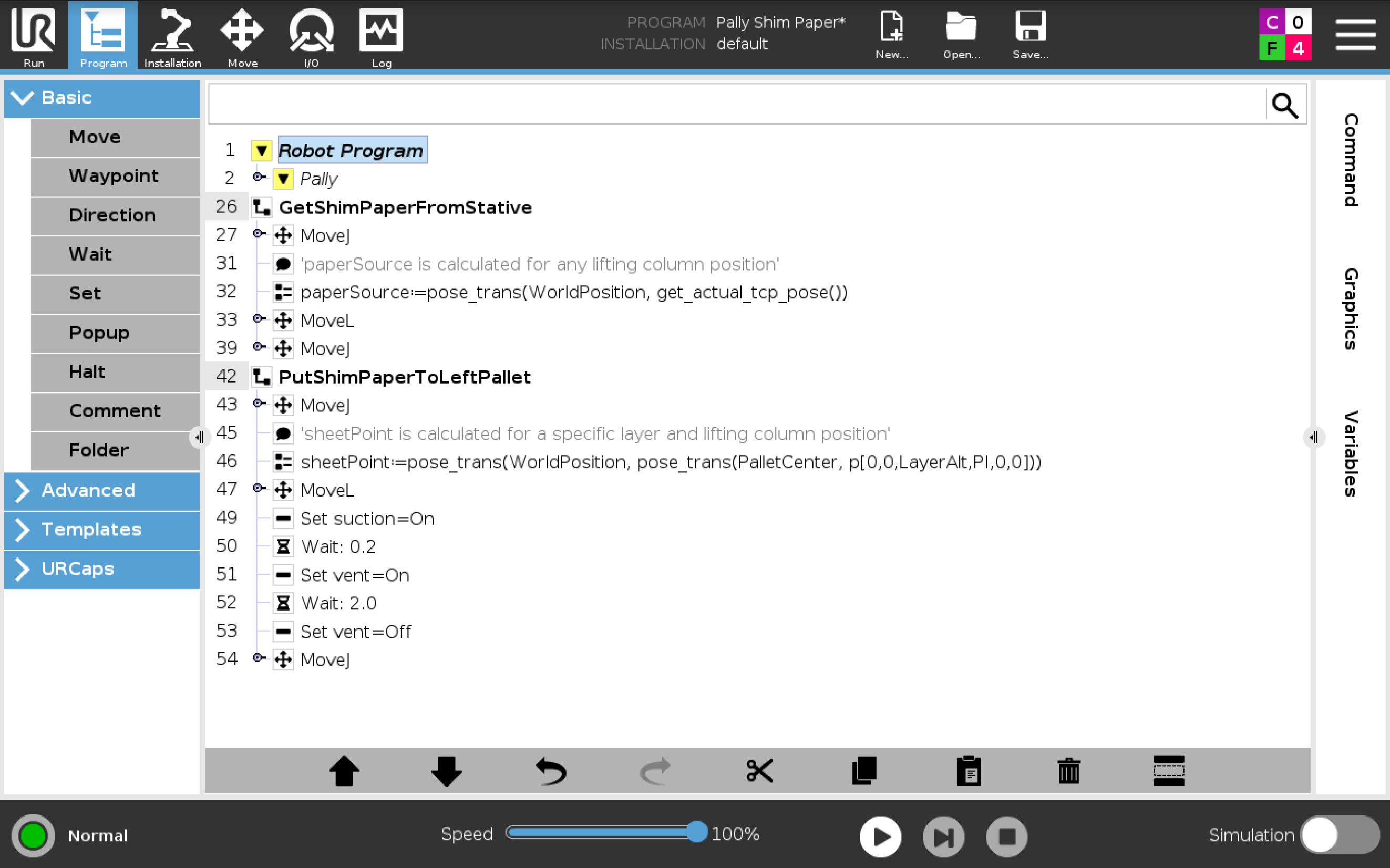
GetShimPaperFromStative and PutShimPaperToLeftPallet code added into the program tree
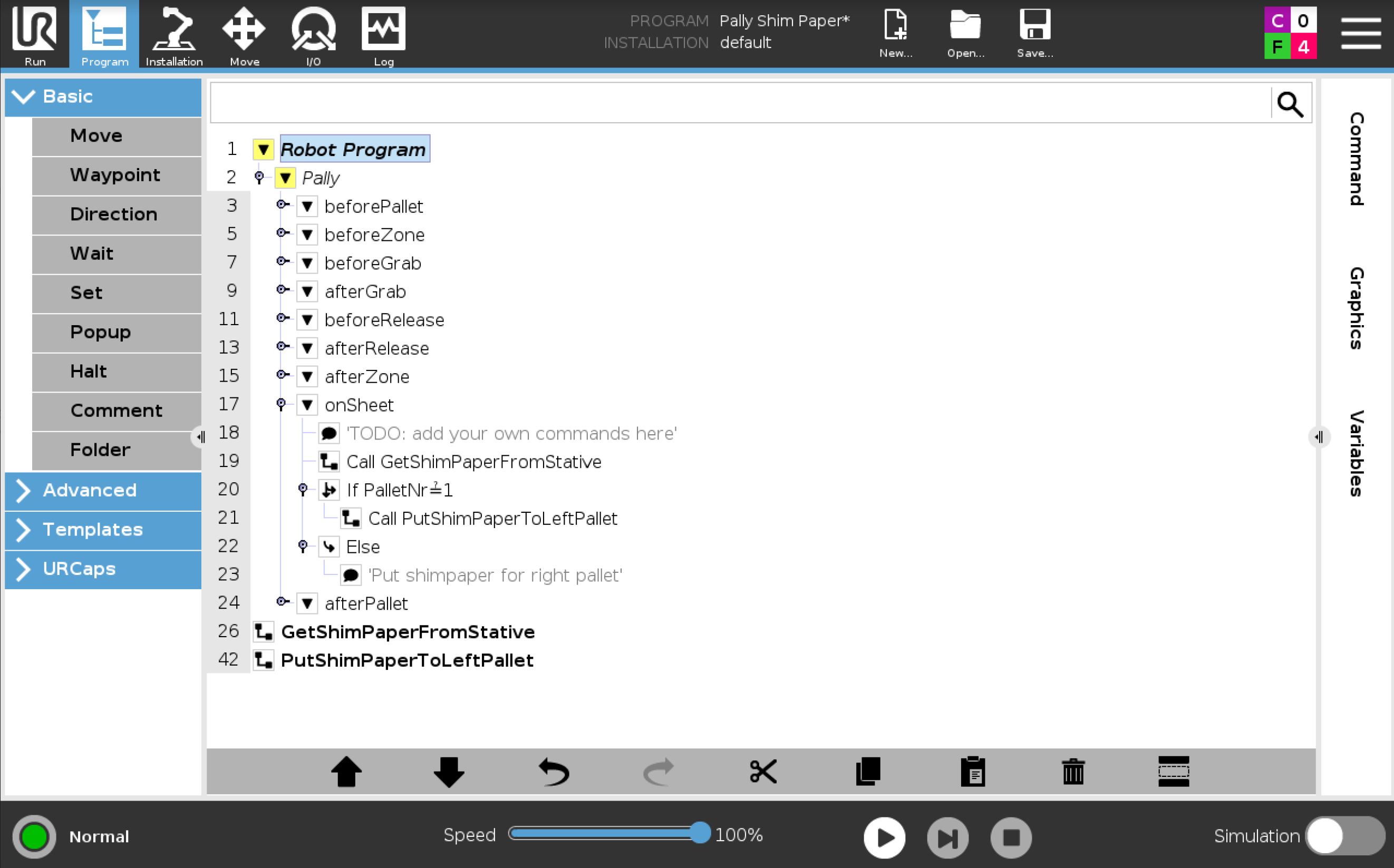
GetShimPaperFromStative and PutShimPaperToLeftPallet sub call from onSheet Callback
Including example programs
GetShimPaperFromStative
PutShimPaperToLeftPallet
Use example programs as SubPrograms in the onSheet() callback, see photos (Program node example1 and Program node example2).
The robot picks a paper from the paper source, then moves it on the top of the current layer of the selected pallet (left pallet in this example).
Important things here:
calculate the altitude of the paper source when the robot is on a lifting column: use the global Pally variable "WorldPosition" as shown in the example:
paper_source = pose_trans(WorldPosition, get_actual_tcp_pose())
movel(paper_source)
calculate the shim paper position on the pallet by using the global Pally variables "WorldPosition" (lifting column only), "PalletCenter", and "LayerAlt"
If you move the lifting column in the shim paper callback, don’t forget to move it back to the position where it was before picking the shim paper:
OnSheet callback:
my_last_pos = get_liftkit_position()
[…] do shim paper pick and place
move_liftkit(my_last_pos)
(This works with Ewellix LiftKit. For other lifting column types, please refer to the lifting column user manual)
sheet_point = pose_trans(WorldPos, pose_trans(PalletCenter, p[0,0,LayerAlt, 3.1415, 0, 0]))
movel(sheet_point)
In this simple example, the gripper is exactly at the center point of the shim paper.
In order to have an offset from the center point, add nonzero values for the x and y coordinates in the transformation as shown below:
sheet_point = pose_trans(WorldPos, pose_trans(PalletCenter, p[X, Y, LayerAlt, 3.1415, 0, 0]))
where X and Y (The unit is meter) are the corresponding distances of the TCP from the center point of the shim paper (in the Cartesian coordinate system of the current TCP). Otherwise use 0, 0 so the paper center will exactly match the pallet center.
When using the URScript function pose_trans() keep the following best practices in mind:
“The first argument, p_from, is used to transform the second argument, p_from_to, and the result is then returned. This means that the result is the resulting pose, when starting at the coordinate system of p_from, and then in that coordinate system moving p_from_to.” (URScript Manual)
Practical examples:
move the gripper in the gripper coordinate system:
pose_trans( get_actual_tcp_pose(), p[0, 0, 0.1, 0, 0, 0] )
move the gripper in the base coordinate system
pose_trans( p[0, 0, 0.1, 0, 0, 0], get_actual_tcp_pose() )
move the gripper in the coordinate system defined by the pallet calibration (with floor correction)
pose_trans( p[0, 0, 0.1, 0, 0, 0], pose_trans(pose_inv(PalletCenter), get_actual_tcp_pose())
Download
Download